Peaslee & Nirenberg at 491-492. Lemke, Lins and Picard, Mortgage-Backed Securities, 4:20 (Thomson West, 2014 ed.). Peaslee & Nirenberg at 4. Peaslee & Nirenberg at 444-445. Peaslee & Nirenberg at 436. Peaslee & Nirenberg at 445. Lemke, Lins and Picard, Mortgage-Backed Securities, 4:21 (Thomson West, 2014 ed.). Did Financiers Truly Get Double-Duped with Re-REMIC Ratings?, HousingWire May 19th, 2010 Silverstein, Gary J.
Tax Management Inc.: Securities Law Series (2007 ): A-54. Silverstein at A-54, A-55. Silverstein at A-55. Peaslee & Nirenberg, 44. Peaslee & Nirenberg at 1309. Peaslee & Nirenberg at 497-498. Peaslee & Nirenberg at 441. Peaslee & Nirenberg at 495. Lynn, Theodore S., Micah W. Bloomfield, & David W. Lowden. Property Financial Investment Trusts.
29. Thomson West (2007 ): 6-22. Peaslee & Nirenberg, 501. Silverstein, A-48. Peaslee & Nirenberg, 13 Peaslee & Nirenberg at 504, 581 Peaslee & Nirenberg at 504 Peaslee & Nirenberg at 505-506. Peaslee & Nirenberg at 44,841.
For a number of factors, mortgage-backed securities are safe investments. The likelihood of in fact losing money is considerably lower than it would be if you bought the stock exchange, for instance. Nevertheless, the financial investment isn't without its downsides. Let's gone through some of this. MBS tend to be fairly safe financial investments.
government. Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac are privatized enterprises, but due to the fact that they've been in government conservatorship given that late 2008 and have an offer to be backed in specific situations by the Federal Real Estate Financing Agency, they have a somewhat implied federal government warranty. If properties are foreclosed upon, it's the obligation of the bond backer to make mortgage investors whole.
If the housing market takes a downturn and individuals begin leaving houses on which they owe more than the homes deserve, that's asking for trouble if enough people default. On the other hand, people will quit a great deal of other things to ensure they have a roofing over their head, so investing in home mortgages is still relatively safe, even in this circumstance.
Top Guidelines Of What Is The Percentage Of People Who Pay Off Mortgages
The downside to buying home mortgages is that there's an inverse relationship between the level of safety and the benefit. You'll acquire a greater rate of development out of a stock if it achieves success, however there is likewise more prospective for a loss. Since the development rate is lower for mortgage-backed securities, something you need to fret about is exceeding inflation.
Inflation risk is absolutely something to believe about. There's likewise a prepayment risk. It's advantageous for a customer to settle the mortgage as soon as possible in order to save money on interest. However, those purchased MBS do not like prepayment because it implies you're getting less interest, which has a direct impact on the amount of return you can anticipate to get - how did clinton allow blacks to get mortgages easier.
The threat that the value of a set income security will fall as a result of a change in rate of interest. Mortgage-backed securities tend to be more conscious changes in rate of interest than other bonds since changes in interest rates affect both the mortgage-backed bond and the home loans within it.
The danger that a security's credit rating will change, resulting in a decrease in worth for the security. The measurement of credit risk typically thinks about the risk of default, credit downgrade, or modification in credit spread. The danger that a security will not have significant demand, such that it can not be offered without considerable deal costs or a decrease in worth.
The threat that inflation will erode the genuine roi. This happens when costs rise at a greater rate than financial investment returns and, as an outcome, cash purchases less in the future. The threat that a change in the total market environment or a particular occurrence, such as a political incident, will have a negative influence on the price/value of your investment.
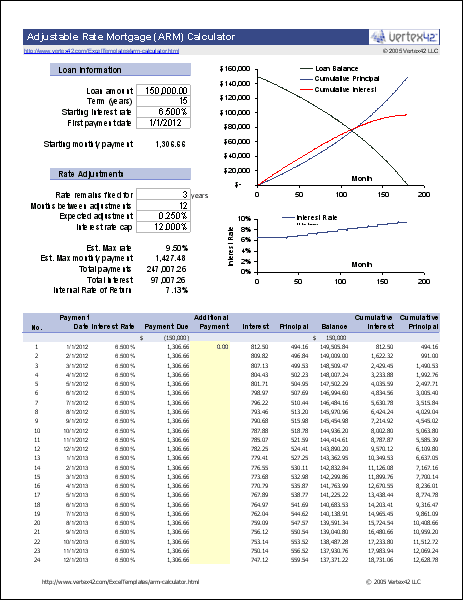
Pools of home loans are the security behind mortgage-backed securities-- MBS. Mortgage-backed securities are a major element of the bond market and numerous mutual fund will have a portion of holdings in MBS. There are likewise funds, of all fund types, that only purchase home mortgage pool securities. The main kind of mortgage securities are stemmed from pools of home loans guaranteed by one of the indicated or specific government mortgage http://andrelolm937.bravesites.com/entries/general/excitement-about-what-are-the-interest-rates-on-30-year-mortgages-today agencies.
Our Why Do Banks Make So Much From Mortgages Statements
A lot of company MBS are established as pass-through securities, which suggests that as property owners with home loans in the swimming pool backing an MBS make primary and interest payments, both principal and interest are paid to MBS investors. There are both shared funds and exchange-traded funds-- ETFs-- that mainly buy mortgage-backed securities.
The finance and financial investment associated sites regularly publish leading funds by classification and these lists would be a great location to begin research study into home mortgage focused bond funds. Taxable bond funds of all types may own MBS. Considering that agency MBS have implicit or implied U.S. government backing, bond funds billed as government bond funds frequently own a significant quantity of mortgage securities.
A fund will note its leading holdings on its websites and if those holdings consist of GNMA, FNMA and FMAC bonds, the fund purchases mortgage swimming pool securities. An alternate way to invest in home loan pools is with home mortgage real estate financial investment trusts-- REITs. Home mortgage REITs own leveraged pools of mortgage securities.
REIT shares trade on the stock market and can be purchased and offered like any stock or ETF. Some home loan REITs exclusively own agency MBS and others hold a mix of firm and MBS from non-agency mortgage swimming pools.
This spreadsheet was originally put together to help decide to either sell home mortgages that were stemmed, or keep them. It can likewise be utilized to help with the decision to acquire a pool of whole loans, or a securitized mortgage pools. 2 different concepts of return are referred to in this post.
on a pool of mortgages is calculated with the following formula: is the rates of interest that makes today value of the overall money streams equivalent to the initial financial investment. Excel makes it simple for us to determine IRR with the integrated in function IRR(). IRR uses an iteration process that attempts various rates of return up until it finds a rate that satisfies this formula (as a faster way I utilize the Excel NPV function): One of the major differences between the two is that HPR lets the user forecast what rate money circulations will be reinvested at in the future, while IRR presumes that all capital will be reinvested at the IRR rate.
Why Do People Take Out Second Mortgages Things To Know Before You Buy
More on that latter. The input cells remain in yellow (as are all my spreadsheets). After entering the beginning principal balance, we go into the gross interest rate. Next is servicing. Servicing is from the viewpoint of the owners or buyers of the pool. If this were a purchase of a swimming pool of whole loans or securitized home mortgages, we would go into the maintenance rate (how to reverse mortgages work if your house burns).
In this example, we are presuming that we stemmed the loans and are now choosing if we desire to hold them, or offer them to FNMA. If we keep them (as in our example) the servicing rate is not subtracted from the gross, due to the fact that we will be getting the gross rate.